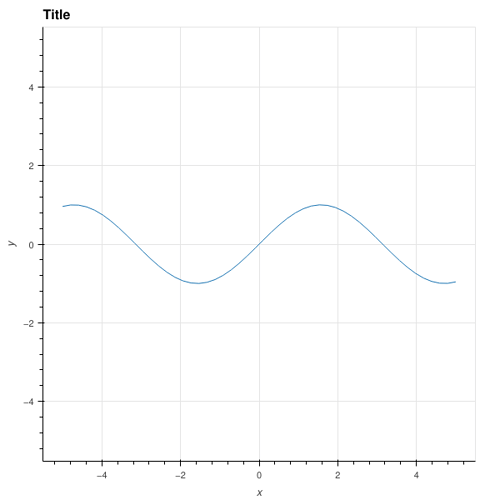
I have a class which uses Bokeh to create a custom plot. Now, I’d like to plot a vector field. Bokeh doesn’t have any function to help doing that (yes, I’ve seen the quiver example but it’s no quivers without arrow heads), but holoviews does: VectorField.
So I told myself: I can use holoviews to generate the glyph and append it to my custom plot:
from bokeh.plotting import figure, show
from bokeh.io import output_notebook
import numpy as np
import holoviews as hv
class MyPlot:
def _get_mode(self):
""" Verify which environment is used to run the code. """
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15411967/how-can-i-check-if-code-is-executed-in-the-ipython-notebook
try:
shell = get_ipython().__class__.__name__
if shell == 'ZMQInteractiveShell':
return 0 # Jupyter notebook or qtconsole
elif shell == 'TerminalInteractiveShell':
return 1 # Terminal running IPython
else:
return 2 # Other type (?)
except NameError:
return 3 # Probably standard Python interpreter
def __init__(self, series, **kwargs):
if self._get_mode() == 0:
output_notebook(
hide_banner=True
)
self.fig = figure(
title = "Title",
x_axis_label = "x",
y_axis_label = "y",
tools = "pan,wheel_zoom,box_zoom,reset,hover,save",
match_aspect = True
)
for k, v in series.items():
if k == "line":
self.fig.line(*v)
elif k == "vector":
vectorfield = hv.VectorField(v)
p = hv.render(vectorfield, backend='bokeh')
self.fig.renderers.append(p.renderers[0])
def show(self):
show(self.fig)
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50)
y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
uu, vv = -np.sin(yy), np.cos(xx)
magnitude = np.sqrt(uu**2 + vv**2)
angle = np.arctan(vv / uu)
data = {
"line": [x, np.sin(x)],
"vector": [xx, yy, angle, magnitude]
}
m = MyPlot(data)
m.show()
As you can see, there is a line plot, but there is no vector plot. Strangely, the vector plot renderer is present, as we can see from:
m.fig.renderers
What can I do to show the vector field (the second renderer)?